Geotrichum candidum Link, (1809)
Sour rot
Sour rot
- class. : Fungi, Ascomycota, Saccharomycetes, Saccharomycetidae, Saccharomycetales, Dipodascaceae
- English name: Sour rot
- English name: Sour rot
This yeast-like fungus is associated with liquid rots on fruits, especially affecting field tomatoes grown flat and intended for industry. It is more rarely found on fruits from trellised crops intended for the fresh market. It is a saprophyte widely present in the environment of tomato crops that is able to attack green or ripe fruits at the slightest opportunity.
- Symptoms
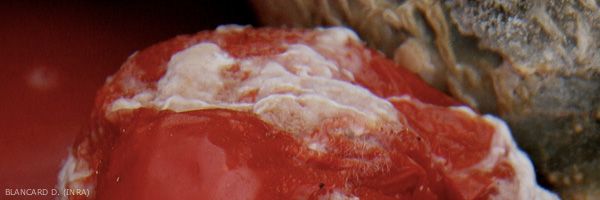
It produces moist and fatty lesions appearing at the level of wounds or the stalk scar of the fruits. These lesions evolve rapidly on mature fruits, the epidermis of which ends up splitting, causing the juice to flow. A whitish and dense mucus sometimes covers the tissues locally (figure 1); it corresponds to the development of colonies of G. candidum . Within the latter, septate mycelium carrying chain arthrospores that end up disarticulating are easily observable under a light microscope (figure 2).
It should be noted that a characteristic acid odor accompanies this rot; it reflects a relatively low pH of the flesh of the fruit, of the order of 4.
Note that the affected green fruits remain firm longer, but they end up experiencing a fate comparable to ripe fruits when fully invaded.
Generic protection methods are available at the following link .
Generic protection methods are available at the following link .






