History
Favus usually begins on the scalp, often in childhood, and persists for many years as unsightly, crusted plaques. According to the severity of the disease, the following three main stages are described:
-
First stage: Only erythema of the scalp is seen, primarily around follicles. Hairs are not loose or broken.
-
Second stage: Formation of scutula is seen with the beginning of hair loss.
-
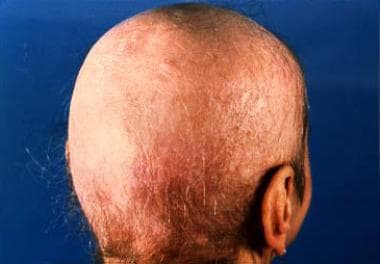
Third stage: The most severe stage involves large areas of the scalp (at least one third); extensive hair loss, atrophy, and scarring result. Formation of new scutula at the periphery of plaques is common.
It may also be seen elsewhere, including on the scrotum. [10]
Physical Examination
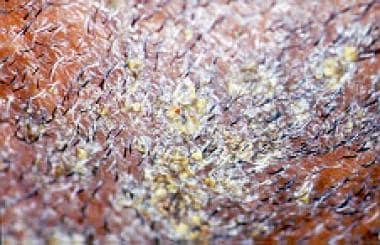
The scutulum, a yellow cup-shaped crust that surrounds a hair and pierces its center, is characteristic. Scutula form a dense plaque, each composed of mycelia and epidermal debris. Often, a secondary bacterial infection occurs in the plaque. Plaque removal leaves an erythematous moist base. The dense masses of yellow crusts may be solitary or numerous, and in patients who are severely affected, involve the entire scalp. A mousy odor typically is present. Glabrous skin may show similar yellow crusting. [21]
On glabrous skin, favus is a papulovesicular and papulosquamous eruption in which typical scutula may be evident. As an onychomycosis, tinea favosa resembles other forms of tinea unguium.
In addition to typical scutular favus on the scalp, several atypical manifestations of favus have been described.
Favus pityroides mimics dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis. Numerous small-to-large scales are present. On the surface, scales are loose; however, deeper layers are attached strongly to the base. Removal of scales uncovers reddish, moist, and scarring areas of skin.
Favus psoriasiformis is a psoriasis-imitating favus, both on the scalp and on glabrous skin. Instead of yellowish scutula, patients present with whitish scales mimicking the typical lesions of psoriasis.
Favus follicularis is characterized by cone-shaped wax-colored papules around the follicles. Hair shows the typical features of favus.
Favus impetigoides is characterized by yellowish (honey-colored) crusts imitating impetigo that are located on the scalp. Frequently, they form larger plaques that do not improve with antibacterial treatment. The characteristic mousy odor and dull hair suggest the diagnosis of favus.
Favus papyroides is characterized by small loci on the scalp that are covered by a brittle substance similar to parchment. Beneath, typical small scutula may be present.
Favus herpetiformis is an atypical variant of favus corporis. Round, erythematous, scaling plaques with small papules, vesicles, pustules, and/or crusts on the border are located on the trunk and extremities. This form of favus shows an annular shape and resembles the lesions typical of tinea corporis.
See the images below.
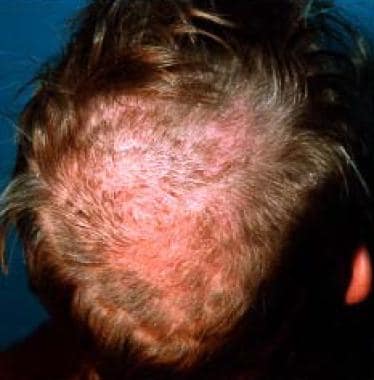 Tinea favosa of the scalp shows erythematous lesions with pityroid scaling. Some hairs are short and brittle.
Tinea favosa of the scalp shows erythematous lesions with pityroid scaling. Some hairs are short and brittle.
-
Tinea favosa of the scalp shows erythematous lesions with pityroid scaling. Some hairs are short and brittle.
-
Favus of the scalp shows extensive lesions with scarring alopecia.
-
Typical fluorescence under Wood lamp examination.
-
Favus, wax montage. Courtesy of Professor Dr Feliks Wasik, Dermatology, Medical University of Wroclaw, Poland.
-
Black man, aged 45 years, with favuslike yellow crusting of scalp. Potassium hydroxide and fungal culture were negative.
-
Culture of Trichophyton schoenleinii on Sabouraud agar. Courtesy of Anna Pawlowicz, PhD, and Professor Barbara Raszeja-Kotelba, MD, Dermatology, University School of Poznan, Poland.
-
Culture of Trichophyton schoenleinii on Sabouraud agar. Note pleomorphism of the culture. Courtesy of Anna Pawlowicz, PhD, and Professor Barbara Raszeja-Kotelba, MD, Dermatology, University School of Poznan, Poland.
-
Microculture of Trichophyton schoenleinii shows dichotomic branching and terminal swelling. Light-field microscopy, original magnification X 1000. Courtesy of Anna Pawlowicz, PhD, and Professor Barbara Raszeja-Kotelba, MD, Dermatology, University School of Poznan, Poland.
-
Microculture of Trichophyton schoenleinii shows characteristic dichotomic branching. Light-field microscopy, original magnification X 1000. Courtesy of Anna Pawlowicz, PhD, and Professor Barbara Raszeja-Kotelba, MD, Dermatology, University School of Poznan, Poland.
-
Microculture of Trichophyton schoenleinii shows numerous terminal chlamydospores. Light-field microscopy, original magnification X 1200. Courtesy of Anna Pawlowicz, PhD, and Professor Barbara Raszeja-Kotelba, MD, Dermatology, University School of Poznan, Poland.
-
Infected hair filled with hyphae shows bubbles of gas and gas tunnels (light field microscopy, original magnification X 2300).