Abstract
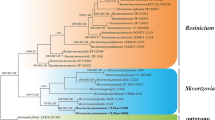
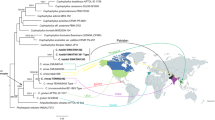
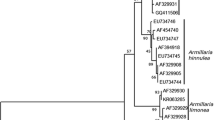
A new holomorphic species, Mariannaea dimorpha, is described and illustrated. The verticillate conidiophores, phialidic conidiogenous cells and aseptate microconidia that form imbricate chains indicate that it belongs to the genus Mariannaea. Sequence analyses of the combined internal transcribed spacer (ITS) and partial large subunit ribosomal DNA (28S rDNA) confirmed its taxonomic position and revealed its distinction from any morphologically similar species. In addition, the teleomorph of M. samuelsii is reported for the first time and its epitype is designated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banning JL, Weddle AL, Wahl GW III, Simon MA, Lauer A, Walters RL, Harris RN (2008) Antifungal skin bacteria, embryonic survival, and communal nesting in four-toed salamanders, Hemidactylium scutatum. Oecologia 156(2):423–429
Cai L, Kurniawati E, Hyde KD (2010) Morphological and molecular characterization of Mariannaea aquaticola sp. nov. collected from freshwater habitats. Mycol Prog 9:337–343
Carris LM, Glawe DA, Smyth CA, Edwards DI (1989) Fungi associated with populations of Heterodera glycines in two Illinois soybean fields. Mycologia 81(1):66–75
Castañeda Ruíz RF, Iturriaga T, Minter DW, Abarca GH, Stadler M, Saikawa M, Fernández R (2009) Two new anamorphic fungi and some microfungi recorded from ‘El Ávila’, Venezuela. Mycotaxon 107:225–237
Cunningham CW (1997) Can three incongruence tests predict when data should be combined? Mol Biol Evol 14:733–740
Degenkolb T, Kirschbaum J, Brückner H (2007) New sequences, constituents, and producers of peptaibiotics: an updated review. Chem Biodivers 4(6):1052–1067
Fabian K, Anke T, Sterner O (2001) Mariannaepyrone—a new inhibitor of thromboxane A2 induced platelet aggregation. Z Naturforsch C 56(1–2):106–110
Fukuda T, Sudoh Y, Tsuchiya Y, Okuda T, Fujimori F, Igarashi Y (2011) Marianins A and B, prenylated phenylpropanoids from Mariannaea camptospora. J Nat Prod 74(5):1327–1330
Gams W, Hoekstra ES, Aptroot A (1998) CBS course of mycology, 4th edn. Baarn, The Netherlands, pp 1–165
Gräfenhan T, Schroers H-J, Nirenberg HI, Seifert KA (2011) An overview of the taxonomy, phylogeny, and typification of nectriaceous fungi in Cosmospora, Acremonium, Fusarium, Stilbella, and Volutella. Stud Mycol 68:79–113
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequences alignment editor analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Han YF, Liang JD, Liang ZQ (2007) Paecilomyces clavisporus and Mariannaea elegans var. punicea—two newly recorded taxa of filamentous Fungi in China. J Fungal Res 5(1):1–3
Hirooka Y, Rossman AY, Samuels GJ, Lechat C, Chaverri P (2012) A monograph of Allantonectria, Nectria, and Pleonectria (Nectriaceae, Hypocreales, Ascomycota) and their pycnidial, sporodochial, and synnematous anamorphs. Stud Mycol 71:1–210
Huang YH (2009) Study on soil moniliaceous hyphomycetes diversity of partial areas of Tibet. MS thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, pp 1–117
Liu H, Skinner M, Parker BL, Brownbridge M (2002) Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes), and other entomopathogenic fungi against Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae). J Econ Entomol 95(4):675–681
Luangsa-ard JJ, Hywel-Jones NL, Samson RA (2004) The polyphyletic nature of Paecilomyces sensu lato based on 18S-generated rDNA phylogeny. Mycologia 96(4):773–780
Luo J, Zhuang WY (2010a) Three new species of Neonectria (Nectriaceae, Hypocreales) with notes on their phylogenetic positions. Mycologia 102(1):142–152
Luo J, Zhuang WY (2010b) Chaetopsinectria (Nectriaceae, Hypocreales), a new genus with Chaetopsina anamorphs. Mycologia 102:976–984
Nirenberg HI (1976) Studies on the morphologic and biologic differentiation in Fusarium section Liseola. Mitt Biol Bundesanst Land- Forstw 169:1–117
Okuda T, Yamamoto K (2000) Materials for the fungus flora of Japan (56) Mariannaea camptospora and M. elegans var. punicea from Japan. Mycoscience 41(4):411–414
Page RD (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comp Appl Biosci 12(4):357–358
Qin CP, Wang XR, Tian YQ, Wang L (2010) Study on the secondary metabolites from Mariannaea camptospora SIIA-F12361. Chinese J Antibiot 35(11):877–880
Rehner SA, Samuels GJ (1994) Taxonomy and phylogeny of Gliocladium analyzed from nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol Res 98:625–634
Rogerson CT, Stephenson SL (1993) Myxomyceticolous Fungi. Mycologia 85(3):456–469
Rossman AY, Samuels GJ, Rogerson CT, Lowen R (1999) Genera of Bionectriaceae, Hypocreaceae and Nectriaceae (Hypocreales, Ascomycetes). Stud Mycol 42:1–248
Rossman AY, Seifert KA, Samuels GJ, Minnis AM, Schroers HJ, Lombard L, Crous PW, Põldmaa K, Cannon PF, Summerbell RC, Geiser DM, Zhuang WY, Hirooka Y, Herrera C, Salgado-Salazar C, Chaverri P (2013) Genera in Bionectriaceae, Hypocreaceae, and Nectriaceae (Hypocreales) proposed for acceptance or rejection. IMA Fungus 4(1):41–51
Samson RA (1974) Paecilomyces and some allied hyphomycetes. Stud Mycol 6:1–117
Samson RA, Bigg WL (1988) A new species of Mariannaea from California. Mycologia 80(1):131–134
Samuels GJ, Seifert KA (1991) Two new species of Nectria with Stilbella and Mariannaea anamorphs. Sydowia 43:249–263
Schroers HJ, Geldenhuis MM, Wingfield MJ, Schoeman MH, Yen YF, Shen WC, Wingfield BD (2005) Classification of the guava wilt fungus Myxosporium psidii, the palm pathogen Gliocladium vermoesenii and the persimmon wilt fungus Acremonium diospyri in Nalanthamala. Mycologia 97(2):375–395
Seifert KA, Louis-Seize G, Sampson G (2003) Myrothecium acadiense, a new hyphomycete isolated from the weed Tussilago farfara. Mycotaxon 87:317–327
Swofford D (2002) PAUP*: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). version 4b10. Sunderland, Massachusetts, Sinauer Associates
Tang L, Hyun MW, Yun YH, Suh DY, Kim SH, Sung GH (2012a) New record of Mariannaea elegans var. elegans in Korea. Mycobiology 40(1):14–19
Tang L, Hyun MW, Yun YH, Suh DY, Kim SH, Sung GH, Choi HK (2012b) Mariannaea samuelsii isolated from a bark beetle-infested Elm tree in Korea. Mycobiology 40(2):94–99
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Tokumasu S, Aoki T, Oberwinkler F (1994) Fungal succession on pine needles in Germany. Mycoscience 35:29–37
Wang L, Zhuang WY (2004) Designing primer sets for amplification of partial calmodulin genes from penicillia. Mycosystema 23(4):466–473
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic, San Diego, pp 315–322
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions. We are very grateful to Prof. Shuang-Lin Chen for his invaluable help during the field work, Dr. Huan-Di Zheng for technical help, and Prof. Lei Cai and Ms. Fang Liu for providing the culture of M. clavispora. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 31070015, 31270073) and Project for Fundamental Research on Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology of China (no. 2013FY110400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, ZQ., Zhuang, WY. A new holomorphic species of Mariannaea and epitypification of M. samuelsii . Mycol Progress 13, 980 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-014-0980-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-014-0980-4